Difference between RAM And ROM: In the world of computers and digital devices, memory plays a crucial role in determining performance and efficiency. Two of the most common types of memory are RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read-Only Memory). While these terms are familiar to many, understanding the key differences between RAM and ROM is essential for anyone interested in how computers work. Both types of memory have distinct functions, and knowing their roles can help you make informed decisions when buying or upgrading your devices.
This article will explore the fundamental differences between RAM and ROM, how they work, their importance in computing, and much more. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clearer understanding of the crucial roles that RAM and ROM play in modern technology.
What is RAM?
RAM stands for Random Access Memory, and it is one of the most essential components in any computer system. RAM is a type of volatile memory, meaning that it only stores data temporarily while the computer is running. Once the power is turned off, all the information stored in RAM is erased.
How RAM Works
RAM is responsible for temporarily storing data that the CPU (Central Processing Unit) needs to access quickly. Think of RAM as the short-term memory of a computer. Whenever you open a program, file, or web browser, the data associated with that task is loaded into RAM, so the processor can access it swiftly.
For instance, when you’re browsing the web, the data for the website you’re viewing is stored in RAM. As you switch between tabs or open new websites, your computer uses RAM to ensure that everything runs smoothly without delay.
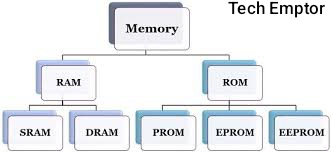
Types of RAM
There are two main types of RAM:
- DRAM (Dynamic RAM): DRAM is the most common type of RAM used in computers. It stores each bit of data in a separate capacitor within an integrated circuit, and since capacitors tend to leak charge, DRAM needs to be refreshed thousands of times per second.
- SRAM (Static RAM): SRAM is faster and more reliable than DRAM but is also more expensive. Unlike DRAM, SRAM does not need to be refreshed as frequently, which makes it faster.
Use Cases of RAM
RAM is crucial in several scenarios:
- Multitasking: When you’re running multiple applications at the same time, RAM ensures that each program can operate smoothly without causing system slowdowns.
- Gaming: High-end games rely on fast RAM to store game data and allow for smooth, real-time interactions.
- Video Editing and Graphic Design: These tasks require a significant amount of temporary memory to store large files and quickly access data.
How RAM Impacts System Performance
The amount of RAM in a computer directly affects its performance. More RAM allows for better multitasking and faster processing speeds. This is why upgrading your RAM can significantly improve your computer’s performance, especially for tasks that involve intensive software, like gaming or video editing.
What is ROM?
ROM stands for Read-Only Memory, and as the name suggests, it is a type of memory where data is permanently written. Unlike RAM, ROM is non-volatile, which means the information stored in it remains intact even after the computer is powered off. This makes ROM ideal for storing the firmware or essential programs that a computer needs to function.
How ROM Works
ROM contains pre-programmed instructions that are necessary for a computer or device to boot up and operate. Unlike RAM, which is wiped clean after each session, ROM retains its data, making it a crucial component for basic system functionality.
For example, the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), which is responsible for initializing hardware components when a computer starts up, is stored in ROM. Without ROM, your computer wouldn’t know how to start or communicate with its hardware.
Types of ROM
There are several types of ROM, each with its own characteristics:
- PROM (Programmable ROM): PROM can be programmed once after manufacture. After being programmed, the data in PROM cannot be modified.
- EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM): EPROM can be erased and reprogrammed using ultraviolet light, making it more flexible than traditional ROM.
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM): EEPROM can be erased and reprogrammed electronically, offering more versatility than EPROM. It is used in applications where data needs to be updated without removing the memory chip.
Use Cases of ROM
ROM is used in various scenarios where data needs to be permanently stored:
- Firmware Storage: ROM is commonly used to store firmware, the permanent software programmed into a hardware device to enable it to function properly.
- Embedded Systems: Devices like microwaves, televisions, and washing machines use ROM to store the programs that control their operations.
- Bootloaders: The bootloader is a piece of software that loads the operating system of a computer. This is typically stored in ROM to ensure it’s always available.
Why ROM is Crucial for Basic Functioning of a Computer
ROM plays an essential role in the operation of any computing device. By storing vital programs like the BIOS and bootloader, ROM ensures that the device can start up and function as intended, even if the operating system or other components are faulty.
Key Differences Between RAM and ROM
While both RAM and ROM are types of memory used in computing, they serve very different purposes. Here are the key differences between RAM and ROM:
Memory Volatility
- RAM: Volatile memory, meaning it requires power to maintain stored information. Once the power is off, all data is lost.
- ROM: Non-volatile memory, which retains data even after the power is turned off.
Storage Capacity and Purpose
- RAM: Typically has a larger storage capacity and is used for temporary data storage that needs to be accessed quickly by the CPU.
- ROM: Has a smaller storage capacity and is used for storing permanent data required for the basic operation of the device.
Speed and Access Times
- RAM: Much faster than ROM because it is designed for quick data access. This speed is critical for running applications and multitasking.
- ROM: Slower compared to RAM, as it is primarily used for storing data that doesn’t need to be accessed frequently.
Rewrite Capabilities
- RAM: Can be written and rewritten as often as needed, making it perfect for dynamic tasks.
- ROM: Cannot be easily rewritten, with some types of ROM being completely unmodifiable after initial programming.
Power Consumption
- RAM: Consumes more power due to its need for constant refreshing of data.
- ROM: Consumes less power, as it retains data without needing to be constantly refreshed.
Importance of RAM in Daily Computing
In today’s fast-paced computing world, RAM is a vital component for many everyday tasks. The amount of RAM in your computer dictates how efficiently you can run multiple applications, how quickly data can be accessed, and how well your device performs under stress.
How Much RAM is Needed for Various Activities?
- Basic Tasks (Browsing, Word Processing): 4GB to 8GB of RAM is sufficient for these simple tasks.
- Gaming: For gaming, at least 8GB is recommended, though 16GB or more can significantly improve performance in modern games.
- Video Editing and Professional Use: For tasks like video editing or running virtual machines, 16GB to 32GB of RAM is ideal.
Future Trends in RAM Technology
RAM technology continues to evolve, with advancements such as DDR5 (Double Data Rate 5) RAM offering higher speeds, lower power consumption, and increased bandwidth. As software becomes more resource-intensive, the demand for more and faster RAM will continue to grow.
Importance of ROM in Daily Computing
While RAM is essential for the dynamic tasks performed by a computer, ROM holds an equally crucial position in ensuring that a device can start up and function as intended.
ROM’s Role in Firmware and Embedded Systems
ROM is indispensable in embedded systems, where devices like refrigerators, microwaves, and smart home systems rely on it to store the instructions that govern their operations. ROM ensures these devices can perform their tasks without the need for frequent updates or modifications.
Examples Where ROM Plays a Critical Role
- BIOS: The BIOS stored in ROM ensures that a computer can start up and load the operating system.
- Device Controllers: ROM is used in controllers for peripherals like printers and keyboards, storing the necessary software for these devices to communicate with the computer.
How to Choose the Right RAM for Your Needs
Choosing the right amount and type of RAM depends on what you plan to do with your computer. Here are some factors to consider:
- Size: The more RAM, the better your computer can handle multitasking. If you’re a gamer or professional user, opt for 16GB or more.
- Speed: Higher speed RAM offers faster data access, which can improve performance in certain applications.
- Compatibility: Make sure the RAM you choose is compatible with your motherboard and CPU.
Common Misconceptions About RAM
One common misconception is that more RAM always equals better performance. While more RAM can improve multitasking, if you’re not running memory-intensive applications, having excess RAM will not make your computer faster. It’s also important to match your RAM’s speed and size with your CPU and motherboard capabilities for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between RAM and ROM is key to optimizing the performance of your computer or device. RAM is your computer’s short-term memory, handling dynamic tasks and temporary data storage, while ROM is the long-term memory responsible for storing critical instructions that allow your device to boot and function properly. Each has its unique role in computing, and both are essential for the efficient operation of modern devices.
FAQs
What is the difference between RAM and ROM in simple terms?
RAM is temporary memory that is used while a computer is running, while ROM is permanent memory that stores essential instructions for the computer to start up.
Which is more important for gaming: RAM or ROM?
For gaming, RAM is far more important because it allows games to load quickly and run smoothly. ROM, on the other hand, plays no direct role in gaming performance.
Can ROM be upgraded like RAM?
No, ROM cannot be upgraded in the same way that RAM can. ROM is typically programmed at the factory and contains essential instructions that are not meant to be altered frequently.
How does RAM affect the performance of a computer?
The more RAM a computer has, the more efficiently it can handle multitasking and run large programs. Insufficient RAM can cause slowdowns, especially when running resource-heavy applications.
Why is ROM considered non-volatile?
ROM is non-volatile because it retains its data even when the computer is powered off, unlike RAM which loses its data once the device is shut down.
